Technology
Contact devices
Bone conduction systemsIntended for ordinary people and persons with conductive hearing impairment (external or middle ear damage). The device works on the basis of resonance, it vibrates the bone behind the hearing organ, this phenomenon generates waves that are transmitted directly to the inner ear and converted into sound.




Cartilage conduction systems
Cartilage conduction is the third pathway by which sound signals are transmitted to the inner ear. These devices work similar way like bone conduction systems.



Audiophone
Devices for amplifying ambient sound.


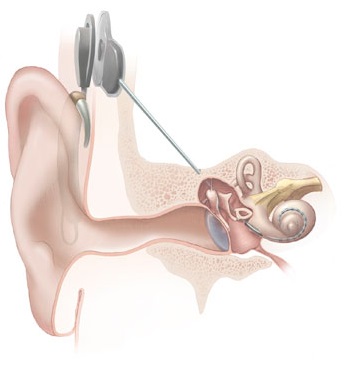
Cochlear implants and Speech processors
The device is implanted under the skin and stimulates the nerves in the inner ear. A combination of a receiving stimulator and a speech processor.

Hearing Loop / Portable Induction Loop System
A type of hearing system for people with hearing aids. The HL system provides magnetic wireless signal that is received by a T-type hearing aid equipped with a "telecoil" element.

Active resonance elements / Body Conduction
Device type, e.g. an exciter that produces vibrations when in contact with the skin. The vibrations are transmitted through the body to the sound canal of the ear, where they are amplified into an audible sound.

Passive resonance elements
A passive resonant element is understood as a (foreign) body - oscillator, resonator, absorber, demodulator, which, under the force of suitable resonance waves typical for the element's material (electromagnetic or mechanical waves of a wavelength different from sound), oscillates and produces vibrations, which further act on a similar principle as bone conduction system or cochlear implant.
The element can be cochlear fluid, brain matter, a "wisdom" tooth, a dental implant, cartilage of the jaw joint or an implanted foreign entity. We are working with the theory that microplastics could act as resonator.
Contactless devices
Audio SpotlightA device that emits an acoustic wave in the form of a direct beam. Persons outside the straight line and direction of the beam do not perceive any sound, it is audible only at the point of final impact.

Directional speaker
A speaker that produces sound (sound waves) in one direction.

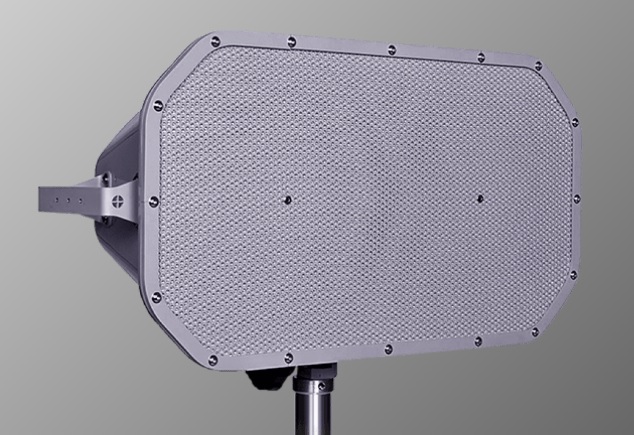
LRAD (Long-range acoustic device)
A long range directional audio device.
Acoustic heterodyne
A device working on the principle of mixing two or more sound sources. At the point of impact or reflection (wall, human body, etc.), the wave frequencies interfere into the audible spectrum, and with appropriate tuning of the source signal, it is possible to create sound at the point of impact - music, speech, etc.
Frey effect devices
Also called microwave auditory effect, is a device, which by emiting short microwave/radio pulses produce sound in the area of auditory cortex. Persons should hear clicks, clicking sound. Currently, there is no evidence about existence of commercional Frey devices.
Ultrasound hearing
A method of hearing frequencies above the audible limit by two-way stimulation: of the hair cells in the inner ear and the resonance effect of the brain mass, which modulates the signal to the audible limit.
Spatial audio and binaural sound
Commercial devices coming with AI head tracking technology providing experience of spatial audio using binaural sound technologies.

